-
Test Service

-
Analysis Service

-
Accreditations/Approvals

- First time visitors
-
- Contact Contact
- JAPANESE
TEST SERVICE
CREEP TEST
CREEP TEST
What is creep testing?
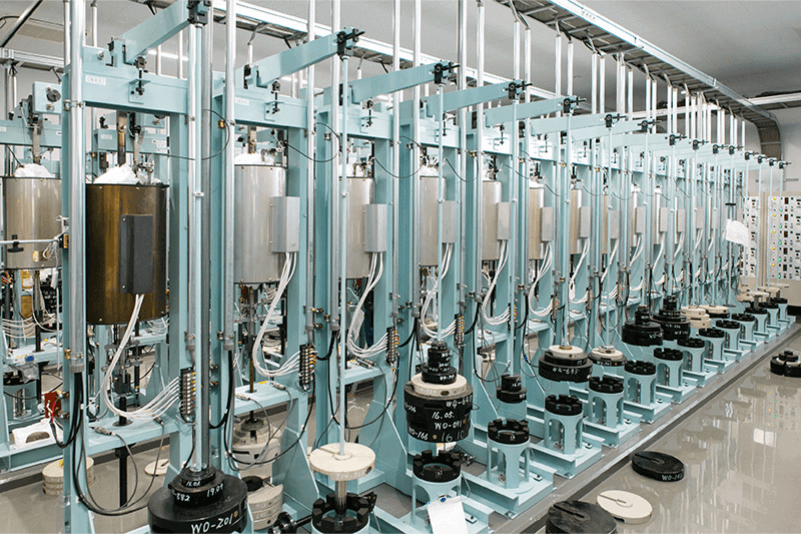
Creep testing is a test in which a specimen heated in an electric furnace is subjected to creep deformation under constant loading. Temperature, strain, and time are continuously measured during testing until the specimen fails. Output from creep testing includes time to rupture and creep curves. The results of creep tests are essential for designing and maintaining equipment that is constantly exposed to high temperature and internal pressure, e.g. steam pipes in power plants and reactors in oil refineries. Creep testing is not only for metallic materials but also for plastic materials, where humidity also affects test results.
What is creep?
Creep is a phenomenon in which a material gradually deforms and eventually ruptures under a static force acting on the material. While creep deformation of metallic materials generally occurs at a temperature above one half of its melting point, it is known that plastic materials can creep at a temperature below room temperature.
Types of creep testing
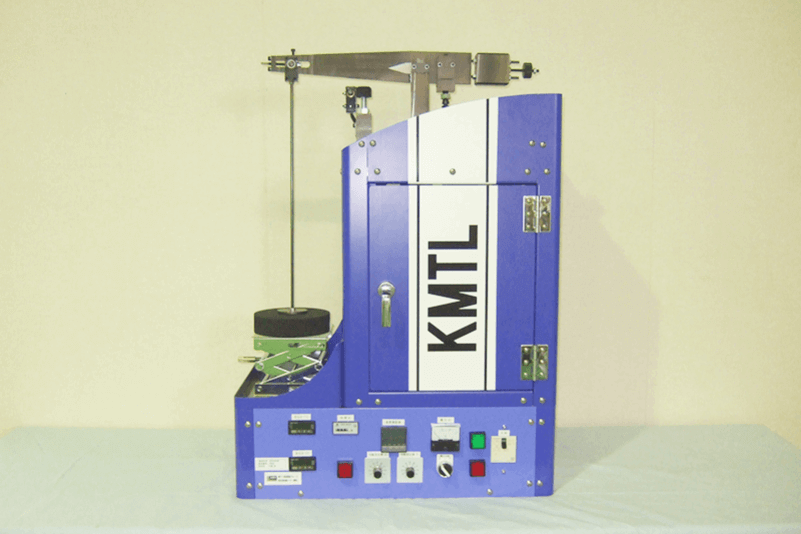
The most common creep test is uniaxial tensile creep testing. Other creep tests include compressive creep testing, torsional creep testing, biaxial and triaxial tensile creep testing, and miniature creep testing such as uniaxial miniature creep testing and small punch creep testing. Furthermore, creep crack propagation testing is conducted to determine the rate of creep crack propagation.
What is creep rupture testing?
What is tensile creep testing?
What is compression creep testing?
Creep testing on plastics
Testing over a long period of time is necessary to estimate creep life. And it is possible to estimate the life over a longer period of time by long-term extrapolation from the relationship between applied stress and time to rupture obtained in a relatively short period of time. However, creep testing of plastic materials often has variation in results and sensitive to temperature and humidity in the environment. In order to improve the accuracy of creep life estimation, it is necessary to increase the number of measurements and obtain data for a period as long as possible.
Creep testing on concrete
Creep testing machine
A uniaxial tensile creep testing machine applies tensile load via a rod to the specimen set inside an electric furnace using a lever-loading mechanism. General creep machines in our laboratory are ones with a lever ratio of 1:10 that can apply load up to 3 tons, but loading up to 5 tons is available. Test temperature is generally between room temperature and 1200℃.
We also design and manufacture creep testing machines from a uniaxial tensile creep machine to miniature creep, small punch creep, and other special creep testing machines. Please contact us for more information, including pricing of testing machines.
JIS standards for creep testing
Creep test methods are specified by different standards. ●Metallic materials: JIS Z 2271 (Metallic materials-Uniaxial creep testing in tension-Method of test), ASTM E 139, ASTM E 292 ●Plastic materials: JIS K 7115 (Plastics−Determination of creep behavior), JIS K 7116 (Flexural creep by three-point loading) ●Concrete: JIS A 1157 (Method of test for compressive creep of concrete)
Contracted creep testing
We perform various types of creep testing on various materials. Creep testing is a very time-consuming test. In order to meet the demands of a number of customers’ requests, we have 428 creep machines, the most of all independent testing laboratories in Japan.
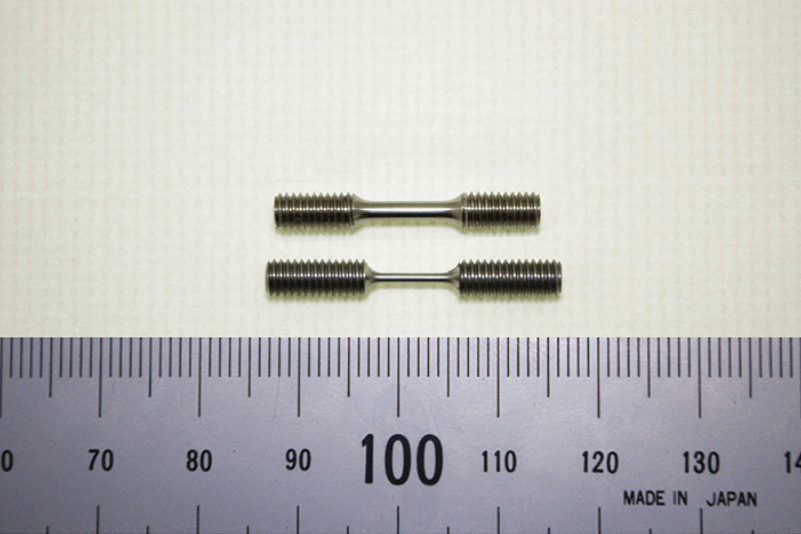
Also, our expertise is focused on miniature testing. One method that has received a great deal of attention is creep evaluation of power plants in operation, that is, a micro specimen is machined from a very small piece sampled from the plant piping and tested to obtain its creep characteristics. In conventional evaluation using a standard-sized specimen, long-time suspension in operation is required because a large sample has to be cut from the piping and repair is necessary after the sample is taken. In addition, some damage to the piping component is unavoidable. To solve this problem, we have developed the Electric Discharge Sampling Equipment for miniature-specimen sampling and miniature testing machines for uniaxial tensile miniature creep testing and small-punch creep testing. With these machines and our miniature testing technology, we provide contracted service for residual life evaluation of structures and plants. Recently, an ultra-miniature creep testing machine has been developed to accommodate even smaller specimens, with which many customers already have placed orders for testing.
Difference between creep testing and fatigue testing
Fatigue testing is a form of mechanical testing in which specimens taken from a material are subjected to a certain type of cyclic loading such as compression, tension, thermal, and ultrasonic loading. To determine the point at which the failure occurs (fatigue limit), multiple specimens taken from the material are tested under different loads, and the number of cycles to failure for each specimen is obtained. With varying loads applied, it is classified as dynamic testing.
On the contrary, creep testing is classified as static testing, where constant load is applied. Testing that combines creep and fatigue testing is called creep fatigue testing.
Basically, creep testing takes a long period of time. It takes several hours of continuous operation at the shortest, and the longest test we experienced at our laboratory required 50,000 hours of continuous operation. For information, the world’s longest creep test record is 14,868 days (approximately 41 years or 356,862 hours) achieved by NIMS (National Institute for Materials Science) in Japan (Guiness World Record).
Creep curve and how to read it
A creep curve is a diagram where strain is on the vertical axis and time is on the horizontal axis. A typical creep curve indicates three different regions: a region immediately after the start of the test where the strain rate is high (primary, or transient, creep region), a region where the strain rate remains constant (the secondary, or steady-state, creep region), and a region where the strain rate increases rapidly to rupture (tertiary, accelerated creep region). The linear relationship seen in the secondary region is called Norton’s law and the slope of the line is called the steady-state creep rate, a constant necessary for creep analysis using FEM.
When the same material is tested, the higher the test temperature or stress, the shorter the time to rupture. Comparing the obtained creep curves shows that the shorter the time to rupture, the larger the slope of the steady creep region (creep rate). Logarithmically plotting the steady-state creep rate (often used in the same meaning of the minimum creep rate) and the time to rupture gives a linear relationship. This relationship is called the Monkman-Grant rule.
Our CREEP TEST
Creep testing at KMTL – Summary
Power generation boilers, steam turbines, and gas turbines are used in high temperature environments. For design and maintenance of such components, it is inevitable to understand the high temperature characteristics of the materials they are made of.
To provide such data, we are always ready to utilize a large number and wide variety of testing machines—special relaxation testing machines, creep fatigue testing machines, multiaxial creep testing machines, miniature creep rupture testing machines, and more—in test rooms controlled at a constant room temperature within ±3℃ variation.

Creep rupture testing machines
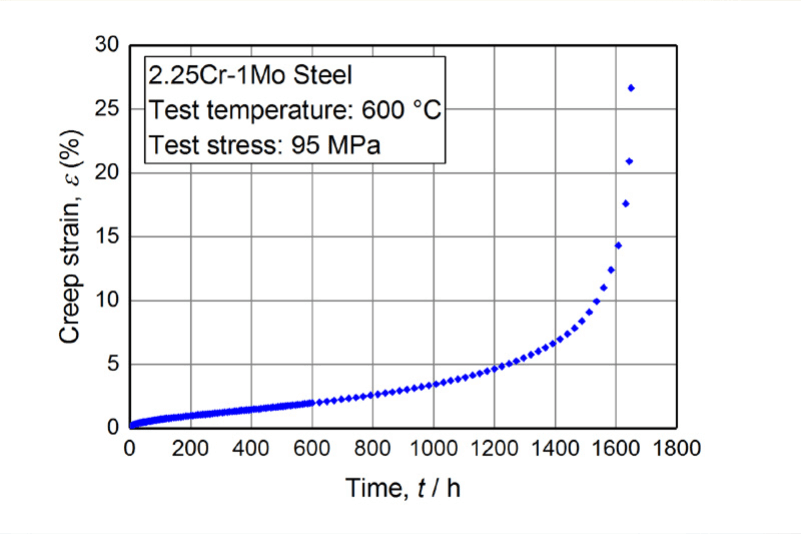
Creep curve

Miniature-creep-rupture testing machine

Miniature-creep test specimen
Main equipment
| Capacity (Single model) | 50kN, 30kN, 15kN, 3kN |
|---|---|
| Test temperature | RT to 1100℃ |
| Capacity | 25 kN |
|---|---|
| Test temperature | 300℃ to 900℃ |
| Capacity | 20 kN |
|---|---|
| Test temperature | 300℃ to 1100℃ |
| Capacity | 1.5 kN |
|---|---|
| Test temperature | 200℃ to 700℃ |
Applicable standard
| JIS Z 2271 |
| ISO 204 |
| ASTM E139 |
| ASTM E292 |
FAQ
FAQ
- Q. What is creep testing?
- A. Creep testing is a test in which a specimen heated in an electric furnace is subjected to creep deformation under constant loading. While testing, temperature, strain, and time are continuously measured until the specimen fails.
- Q. What is creep rupture testing?
- A. Creep rupture testing, also known as stress rupture testing, is a test to determine the time to rupture under specified temperature and stress. The time to rupture is also called the creep strength and used especially to evaluate the remaining creep life of equipment subjected to high temperature.
- Q. What is tensile creep testing?
- A. The most popular creep testing method is uniaxial creep testing, which accounts for 90% of creep tests performed in our laboratory. In a uniaxial creep test, an extensometer is attached to ribs machined at the ends of the reduced section of the specimen to measure elongation.
- Q. What is compression creep testing?
- A. Creep also occurs when a material is compressed. Although the direction of force is exactly opposite in tension and compression, most testing machines only apply tensile load. Compressive creep testing is available at our laboratory using a special fixture designed to convert tensile force to compressive force.
- Q. What is creep testing on plastics?
- A.Creep testing is performed on plastics to evaluate their creep life. Generally, testing requires a long period of time. However, by extrapolation for a long-term prediction from the relationship between applied stress and time to rupture obtained in a relatively short period of time, it is possible to estimate the life for a longer period of time.
- Q. Creep testing on concrete?
- A. Concrete, used to structure high-rise buildings for example, undergo creep at ambient temperature. Creep occurs as fine air bubbles and water content in the concrete change over time due to the weight of the structure itself. Creep testing is essential to understand the safety of a building.
- Q. Does Kobe Material Testing Laboratory undertake subcontracted creep testing?
- A. A wide range of tests are available at Kobe Material Testing Laboratory, including creep tests. If you have any problems with creep testing, please do not hesitate to contact us. Any kind of request is welcome. If interested, refer to the lineup of our testing services.➡TEST SERVICE
- Q. What kind of creep tests does Kobe Material Testing Laboratory conduct?
- A. We perform various types and various materials of creep testing. We have 428 standard uniaxial tensile creep testing machines, the largest number of all independent testing laboratories in Japan.
- Q. What is the difference between creep testing and fatigue testing?
- A. Fatigue testing is a form of mechanical testing that is performed by applying cyclic loading to a specimen. It is classified as dynamic testing. For details, please refer to the page for fatigue testing.
➡CREEP TEST
On the contrary, creep testing is classified as static testing, where constant load is applied.
TEST SERVICE
Test Service
KMTL provides a wide range of testing services including fatigue and creep testing to support safety and security for society at large.





